Foreign trade:The certificate of origin is not as simple as you think. You must know these 12 instructions
In cross-border trade, the ceritificate of origin is increasingly mentioned. As an important document in foreign trade, the certificate of origin is increasingly entering the field of foreign trade negotiations. Since the certificate of origin can bring a certain degree of tariff reduction or exemption, it is also called "paper gold".
What is a certificate of origin?
The certificate of origin is a kind of certification document used to prove the place of manufacture of the export goods. It is the certificate of the "origin" of the goods in international trade. Under certain circumstances, the importing country will give different tariff treatments to the imported goods.
What are the types of certificates of origin in China?
In China, according to the role of the certificate of origin, there are three main types of certificates of origin issued for export goods:
The first category is the non-preferential certificate of origin, which is commonly referred to as the "general certificate of origin". It is a certification document that certifies that the goods are originally produced in China and enjoy the normal tariff (most-favoured-nation) treatment of the importing country, referred to as the CO certificate.
The second category is the preferential certificate of origin, which can enjoy more preferential tariff treatment than the most favored nation treatment, which mainly includes the GSP certificate of origin and regional preferential certificate of origin.
The third category is the professional certificate of origin, which is a certificate of origin specified for a specific product in a particular industry, such as the "Certificate of Origin of Agricultural Products Exported to the EU".
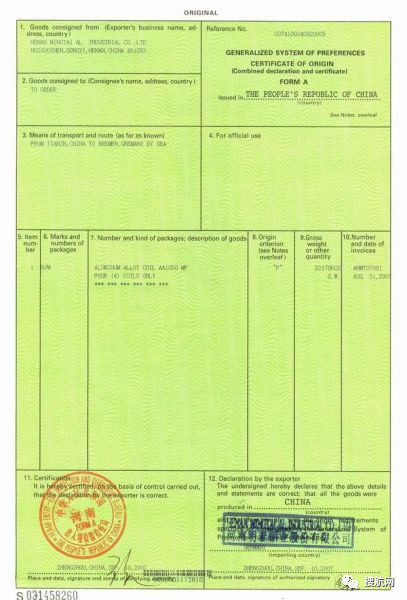
So what are the information and matters needing attention in the preparation of the certificate of origin?
The first column (Exporter):
The name, address, and country of the exporter must be registered by the Inspection and Quarantine Bureau, and its name and address must be consistent with the registration file. Must fill in the detailed address and country name(CHINA) of the exporter in China.
If the export unit is a branch of a company in another country or region, it can be filled in when the applicant requests to fill in the name of the overseas company. However, it is necessary to add ON BEHALF OF (O/B) or CARE OF (C/O) then the name of the overseas company after the name of the exporter in China.
The second column (Consignee):
The name, address and country of the consignee should generally be filled in with the name of the final consignee, that is, the notifier of the bill of lading or the consignee specified in the letter of credit. If the final consignee is unclear or is an intermediary, you can fill in "TO ORDER".
The third column (Means of transport and route)
Fill in the name of the port of loading, the port of destination and the means of transportation (sea, air or land). In case of transshipment, the place of transshipment shall be indicated. The format is "FROM...TO...BY...(VIA...)". Multimodal transport should be explained in stages.
The fourth column (Country/region of destination):
Destination refers to the final arrival of the goods at the port, or country or region, and should generally be consistent with the final consignee (column 2). You cannot fill in the name of the middleman country.
The fifth column (For certifying authority use only):
Special column for visa agency, leave this column blank. Fill in after the issuance of a certificate, the issuing authority issues a certificate, reissues a certificate or adds other declarations.
The sixth column (Marks and numbers):
Marks and numbers
This column should be filled with the complete pattern, text mark and package number listed on the export invoice. If you cannot fill in more than one column, you can fill in the blank space of the seventh, eighth, and ninth column. If it is not enough, you can fill in an additional page. If the pattern text cannot be reproduced, a photocopy can be attached, but it must be stamped with the seal of the issuing authority. If there is no mark, fill in the word N/M. In this case, the words "Made in Hong Kong, Taiwan or other countries and regions" etc. shall not appear.
The seventh column (Number and kind of packages; description of goods):
Number and kind of packages; description of goods
This column should indicate the general name and specific name of the product. After the product name, uppercase English numbers must be added and Arabic numerals and packaging types or units of measurement must be added in parentheses.
If the batch of goods has different varieties, there must be a total number of boxes. A cut-off line (***) should be added at the end to prevent falsified content. Foreign letters of credit sometimes require filling in the contract, letter of credit number, etc., which can be added in the blank space below the cut-off line.
The eighth column (H.S Code):
Commodity code
This column requires a four-digit H.S. tax item number. If the same certificate contains multiple commodities, all corresponding tax item numbers should be filled in.
The ninth column (Quantity):
Quantity and weight
This column should fill in the unit of measurement of the commodity. The gross weight or net weight should be filled in by weight. If the same certificate contains multiple commodities, the quantity must be filled in with the commodity name and commodity code in columns 7 and 8, and some must also fill in the total number.
The tenth column (Number):
Invoice number and date
This column cannot be left blank. It must be filled out in accordance with the commercial invoice of the exported goods applied for. All months are filled in in English. The date in this column should be earlier than or the same as the declaration and issuance date in columns 11 and 12.
The eleventh column (Declaration by the exporter):
This column shall be signed by the applicants who have registered with the visa agency and affixed with the Chinese and English seals of the enterprise. The signature and the seal of the hand-signed person shall not overlap. At the same time fill in the application place and date, the date in this column shall not be earlier than the invoice date (column ten).
The twelfth column (Certification):
The visa agency indicates
The applicant unit fills in the date and place of the visa in this column, and then, the visa holder authorized by the visa agency will sign and seal it.
The date of issuance shall not be earlier than the date of invoice (column ten) and the date of application (column eleven). If a letter of credit requires the name, address, telephone number, fax number, and name of the visa personnel to fill in the name of the issuing authority, it must be carefully checked and required to be accurate.
However, there are some corresponding considerations:
1. FORM A needs to be stamped with the commodity inspection seal and the company's Chinese and English seals. The 11th column covers the seal of the Commodity Inspection Bureau, and the 12th column covers the Chinese and English seals of the company. And each need to be signed. Among them, the company's stamp office signs the stamp of the personnel filing with the Commodity Inspection Bureau.
2. The date on the commercial invoice/packing list provided to the customer shall be based on the date filled in the number and date of invoices in the 10th column.




















